GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT CARS
The car is uniform and indivisible, almost alive organism.
Only at full load capacity of all its components, auto mobile can perform those functions which imposes on Ho Sain. In the car (as in the person) all components constantly interact and ensure its smooth running.
However, as in anatomy, "organism" of the car can be decomposed into large and small components. The car consists of:
· engine;
· powertrain;
· chassis;
· governance arrangements;
· electrical equipment;
· additional equipment;
· body.
The car can long and hard to stand in one place, of purpose, it should rely "feet" on the road, and drive it only when the wheels start to spin the nut. What makes them spin? How does the car engine transmits torque to the wheels? The engine burns the fuel and converts thermal energy of the CDF ranija in rotary movement of the crankshaft, then the rotation is transmitted through the transmission to the drive wheels, which are
element of the vehicle chassis, and... go. While driving the vehicle the driver uses a rudder and brakes (mechanisms of governance), includes light bulb and "bibical" (elektrooporu the study), and, of course, at this time he is sitting in the driver's seat, wear seat belts (extra equipment). All of the above combines the body of a vehicle, without which all units, mechanisms and even sitting
the driver would lay a huge heap in the corner of the garage.
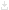
The structure of the car
· a radiator of system of cooling;
· rechargeable battery;
· the breaker the ignition distributor;
· air filter;
· engine;
· vacuum amplifier with the main cylinder of a hydrodrive tor Mosul;
· master cylinder of a hydraulic drive of deenergizing of coupling;
· the steering wheel;
· internal rear-view mirror;
· the back seat;
· rear brake;
· coil spring rear suspension;
· the rear suspension absorber;
· the rear axle;
· driveline;
· front seat;
· external rearview mirror;
· the Parking brake lever;
· the shift lever;
· transmission;
· the clutch pedal;
· the brake pedal;
· the accelerator pedal ("gas");
· steering gear housing;
· front brake;
· coil spring front suspension with shock absorber;
· the fuel pump;
· the oil filter.
The engine is a unit in which the thermal energy of shoyusupov is converted into mechanical energy.
Transmission is intended for transfer and change of crucesignati from the engine to the drive wheels of the vehicle. It includes:
· grip,
· transmission,
· gimbal transmission,
· main gear,
· differential,
· the half-line.
Suspension is designed to move the car on the horn with a certain level of comfort without jolting and vibration and includes:
· front and rear wheel suspension,
· the wheels.
Mechanisms of management serve for change of direction of movement, stopping or Parking of the vehicle. The governance arrangements include:
· steering,
· brake system.
Electrical equipment is designed to provide the potential electrical current of all electric devices of the vehicle, and consists of:
· current sources,
· current consumers.
The additional equipment provides comfortable and safe environment for driver and passengers. An example of complementary equipment can serve: a heater of the vehicle interior, washer and windscreen wipers, electric Windows and much more.
The car is uniform and indivisible, almost alive organism.
Only at full load capacity of all its components, auto mobile can perform those functions which imposes on Ho Sain. In the car (as in the person) all components constantly interact and ensure its smooth running.
However, as in anatomy, "organism" of the car can be decomposed into large and small components. The car consists of:
· engine;
· powertrain;
· chassis;
· governance arrangements;
· electrical equipment;
· additional equipment;
· body.
The car can long and hard to stand in one place, of purpose, it should rely "feet" on the road, and drive it only when the wheels start to spin the nut. What makes them spin? How does the car engine transmits torque to the wheels? The engine burns the fuel and converts thermal energy of the CDF ranija in rotary movement of the crankshaft, then the rotation is transmitted through the transmission to the drive wheels, which are
element of the vehicle chassis, and... go. While driving the vehicle the driver uses a rudder and brakes (mechanisms of governance), includes light bulb and "bibical" (elektrooporu the study), and, of course, at this time he is sitting in the driver's seat, wear seat belts (extra equipment). All of the above combines the body of a vehicle, without which all units, mechanisms and even sitting
the driver would lay a huge heap in the corner of the garage.
The structure of the car
· a radiator of system of cooling;
· rechargeable battery;
· the breaker the ignition distributor;
· air filter;
· engine;
· vacuum amplifier with the main cylinder of a hydrodrive tor Mosul;
· master cylinder of a hydraulic drive of deenergizing of coupling;
· the steering wheel;
· internal rear-view mirror;
· the back seat;
· rear brake;
· coil spring rear suspension;
· the rear suspension absorber;
· the rear axle;
· driveline;
· front seat;
· external rearview mirror;
· the Parking brake lever;
· the shift lever;
· transmission;
· the clutch pedal;
· the brake pedal;
· the accelerator pedal ("gas");
· steering gear housing;
· front brake;
· coil spring front suspension with shock absorber;
· the fuel pump;
· the oil filter.
The engine is a unit in which the thermal energy of shoyusupov is converted into mechanical energy.
Transmission is intended for transfer and change of crucesignati from the engine to the drive wheels of the vehicle. It includes:
· grip,
· transmission,
· gimbal transmission,
· main gear,
· differential,
· the half-line.
Suspension is designed to move the car on the horn with a certain level of comfort without jolting and vibration and includes:
· front and rear wheel suspension,
· the wheels.
Mechanisms of management serve for change of direction of movement, stopping or Parking of the vehicle. The governance arrangements include:
· steering,
· brake system.
Electrical equipment is designed to provide the potential electrical current of all electric devices of the vehicle, and consists of:
· current sources,
· current consumers.
The additional equipment provides comfortable and safe environment for driver and passengers. An example of complementary equipment can serve: a heater of the vehicle interior, washer and windscreen wipers, electric Windows and much more.